Calculate your sample size
A sample size calculator is a tool used to determine how many responses or observations are needed to get reliable results from a survey, study, or experiment. People usually search for this when they want accurate data without collecting more information than necessary.
Whether you’re running a survey, doing academic research, or planning market research, choosing the right sample size matters. A sample that’s too small can give misleading results, while a sample that’s too large can waste time and resources.
This guide explains what a sample size calculator is, how it works, and how to use it correctly. You’ll also learn what inputs matter, common mistakes to avoid, and when using a calculator makes sense.
What Is a Sample Size Calculator
A sample size calculator is an online or statistical tool that helps you calculate the number of people, items, or observations needed to represent a larger population accurately.
Instead of guessing how many responses you need, the calculator uses basic statistical inputs like confidence level and margin of error to give a clear number. This helps ensure that your results are reliable and not based on chance.
Sample size calculators are commonly used in:
- Surveys and polls
- Academic and scientific research
- Market and customer research
- Experiments and testing
In simple terms, the tool answers one key question: How many samples do I need for my results to be trustworthy?
Why Sample Size Matters in Research
Sample size matters because it directly affects how accurate and reliable your results are. When the sample is too small, the results can swing widely and may not reflect the real situation. When it’s too large, you may spend extra time and money without gaining much improvement in accuracy.
A proper sample size helps balance precision and effort. It reduces random error and makes your findings more stable. This is why surveys, studies, and experiments rely on sample size calculations instead of guesswork.
Here’s what sample size influences in practice:
- Accuracy. Larger samples usually give results closer to the true value.
- Confidence. You can be more sure your results are not due to chance.
- Cost and time. The right size avoids unnecessary data collection.
Using a sample size calculator helps you pick a number that’s reasonable and statistically sound, based on how precise you want your results to be.
Key Inputs You Need for a Sample Size Calculator
A sample size calculator works by using a few standard inputs. Each input affects the final number, so understanding them helps you use the tool correctly instead of treating it like a black box.
Population Size
This is the total number of people or items you want to study. If you’re surveying customers of a company or students in a school, that full group is the population. For very large populations, the exact size matters less, but it’s still useful when known.
Margin of Error
The margin of error shows how close your results should be to the true value. A smaller margin of error means more precision, but it also increases the required sample size. A larger margin allows more variation and needs fewer responses.
Confidence Level
The confidence level reflects how sure you want to be about your results. Common choices are 90%, 95%, or 99%. Higher confidence means more certainty, but it also requires a larger sample.
Expected Proportion (Variability)
This is an estimate of how responses might be distributed. When you don’t know this in advance, many calculators use a standard value that assumes maximum variation. This approach keeps the result on the safer side.
These four inputs work together. Changing even one of them can noticeably change the sample size, which is why using a calculator is more reliable than guessing.
How a Sample Size Calculator Works (With an Example)
A sample size calculator uses a standard statistical formula to turn your inputs into a practical number. You don’t need to do the math yourself, but understanding the logic helps you trust the result.
At a high level, the calculator combines:
- the confidence level
- the margin of error
- the expected proportion
- and sometimes the population size
These values are used to estimate how many samples are needed so the results stay within your chosen accuracy range.
Simple Example
Let’s say you want to run a survey with:
- a 95% confidence level
- a 5% margin of error
- an unknown response distribution
When you enter these values into a sample size calculator, it returns a sample size that is large enough to keep results reliable even if responses vary widely. If you lower the margin of error or raise the confidence level, the required sample size increases.
When the population size is small and known, the calculator adjusts the result slightly so you don’t oversample. This adjustment helps keep the sample efficient without reducing accuracy.
In short, the calculator translates your accuracy goals into a clear, usable number you can apply to your study.
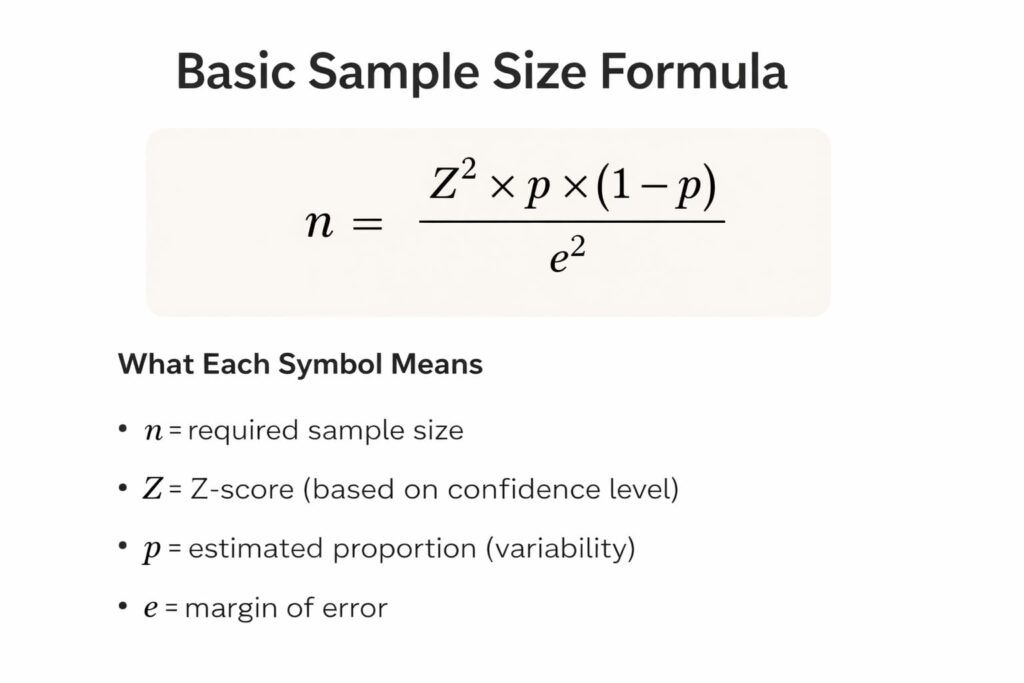
Sample Size Formula (Explained Simply)
Most sample size calculators are based on a standard statistical formula. This formula estimates how many samples are needed to achieve reliable results given a confidence level and margin of error.
The Basic Sample Size Formula
What Each Symbol Means
- n = required sample size
- Z = Z-score (based on confidence level)
- p = estimated proportion (variability)
- e = margin of error
This formula assumes a large or unknown population.
Z-Score Values Used in Sample Size Calculation
| Confidence Level | Z-Score |
|---|---|
| 90% | 1.65 |
| 95% | 1.96 |
| 99% | 2.58 |
These values explain why higher confidence levels require larger samples.
Sample Size Formula for a Known (Finite) Population
When the population size is known and relatively small, calculators apply a finite population correction:
Where:
- n = sample size from the first formula
- N = total population size
This adjustment prevents oversampling when the population is limited.
Using the formula, the calculator determines a sample size that keeps results within ±5% of the true value, 95 times out of 100. You don’t need to calculate it manually. The calculator handles this instantly.
Sample Size Calculator (Quick Reference Table)
This table summarizes the main inputs used in a sample size calculator and explains what each one does. It’s useful if you want a quick refresher before running a calculation.
| Input | What It Means | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Population Size | Total group you want to study | Helps adjust the sample when the group is small |
| Margin of Error | Allowed difference from the true value | Smaller values increase accuracy and sample size |
| Confidence Level | How sure you want to be about results | Higher confidence needs more samples |
| Expected Proportion | Estimated response distribution | Affects how large the sample must be |
| Sample Size | Final number of responses needed | Ensures reliable and usable results |
This reference makes it easier to understand how each setting influences the final sample size before you move on to real-world use.
When to Use a Sample Size Calculator
A sample size calculator is useful whenever you need results that reflect a larger group without collecting data from everyone. It helps you plan studies with confidence and avoid unreliable outcomes.
You should use a sample size calculator when:
- You are designing a survey or poll and want dependable results
- You are conducting academic or scientific research
- You are planning market or customer research
- You are running experiments or tests and need consistent data
It’s especially helpful during the planning stage. Knowing the required sample size early helps you set realistic goals, timelines, and budgets. Instead of adjusting after data collection starts, you begin with a clear target.
Using a calculator also keeps results comparable. When studies follow proper sample size planning, their findings are easier to interpret and trust.
Tips to Choose the Right Sample Size
Choosing the right sample size is not only about plugging numbers into a calculator. A few practical considerations can help you make better decisions and avoid common issues.
Start by being realistic about your goals. If you need very precise results, you’ll need a larger sample. If a general trend is enough, a slightly larger margin of error can reduce the required size.
Keep these points in mind:
- Higher confidence levels always require more samples
- Smaller margins of error increase accuracy but raise costs
- For very large populations, the sample size doesn’t grow much after a point
- When unsure about response distribution, using a conservative estimate is safer
It’s also useful to balance accuracy with available time and resources. A sample size calculator gives you a statistical answer, but you still decide what works best for your situation.
Common Mistakes When Using a Sample Size Calculator
Even with a sample size calculator, mistakes can happen if the inputs are misunderstood or used carelessly. These issues often lead to results that look precise but aren’t truly reliable.
One common mistake is choosing a confidence level without understanding its impact. Setting it too high can inflate the sample size beyond what’s practical, while setting it too low can weaken the results.
Another issue is ignoring the margin of error. Some users select a number without thinking about how much variation they can actually accept. This can either overcomplicate the study or reduce accuracy more than intended.
Other frequent mistakes include:
- Forgetting to adjust for a small, known population
- Assuming any sample size works for all studies
- Treating the calculator result as exact rather than a guideline
Using the calculator thoughtfully, and understanding what each input means, helps avoid these problems and leads to better outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
A good sample size depends on your confidence level, margin of error, and population. There is no single number that works for every study. A sample size calculator helps determine the right value based on these factors.
Sample size can be calculated using a statistical formula that includes confidence level, margin of error, and expected proportion. However, most people use an online sample size calculator to avoid manual errors.
Population size matters more when the group is small and known. For very large populations, the required sample size does not increase much beyond a certain point.
Yes, when used correctly. The calculator follows standard statistical methods, but the accuracy depends on choosing appropriate input values.
Many studies use a 95% confidence level because it balances accuracy and practicality. Higher levels increase certainty but also require larger samples.
Final Thoughts on Sample Size Calculator
A sample size calculator is a practical tool for planning surveys, research, and experiments with confidence. It helps you choose a sample size that balances accuracy, reliability, and available resources.
By understanding the key inputs and avoiding common mistakes, you can use the calculator more effectively instead of relying on guesswork. Whether you’re working on a small survey or a larger study, proper sample size planning leads to clearer and more trustworthy results.
Also read: